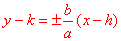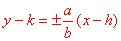Analytic Geometry Formulas
| 1. Circle | (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2 |
center (h, k) radius r |
| 2. Parabola | ||
| (x - h)2 = 4p (y – k) | opens up vertex (h, k) focus (h, k+p) directrix y = k – p |
|
| (x - h)2 = -4p (y - k) | opens down vertex (h, k) focus (h, k-p) directrix y = k + p |
|
| (y - k)2 = 4p (x - h) | opens right vertex (h, k) focus (h + p, k) directrix x = h – p |
|
| (y - k)2 = -4p (x - h) | opens left vertex (h. k) focus (h - p, k) directrix x = h + p |

|
| Ellipse | ||||
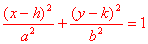
|
center (h, k) a2 - b2 = c2 or a2 = b2 + c2 foci (h - c, k), (h + c, k) sum of distances to foci = 2a major axis is parallel to x-axis = 2a minor axis is parallel to y-axis = 2b eccentricity = c / a vertices (h + a, k), (h - a, k), (h, k + b), (h, k - b) |
|||
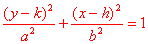
|
center (h, k) a2 - b2 = c2 or a2 = b2 + c2 foci (h, k+c), (h, k-c) sum of distances to foci = 2a major axis is parallel to x-axis = 2a minor axis is parallel to y-axis = 2b eccentricity = c / a vertices (h + b, k), (h - b, k), (h, k + a), (h, k - a) |
|||
| Hyperbola | ||||
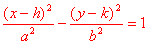
|
center is (h, k) c2 = a2 + b2 vertices (h + a, k), (h - a, k) foci (h + c, k), (h - c, k)
|
|||
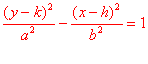
|
center is (h, k) c2 = a2 + b2 vertices (h, k + a), (h, k - a) foci (h, k + c), (h, k - c)
|