df / dx = lim (dx -> 0) (f(x+dx) - f(x)) / dx (right sided)
df / dx = lim (dx -> 0) (f(x) - f(x-dx)) / dx (left sided)
df / dx = lim (dx -> 0) (f(x+dx) - f(x-dx)) / (2dx) (both sided)


 f(t) dt = f(x) (Fundamental Theorem for Derivatives)
f(t) dt = f(x) (Fundamental Theorem for Derivatives)
 c f(x) = c
c f(x) = c
 f(x) (c is a constant)
f(x) (c is a constant)
 (f(x) + g(x)) =
(f(x) + g(x)) =
 f(x) +
f(x) +  g(x)
g(x)
 f(g(x)) =
f(g(x)) = 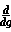 f(g) *
f(g) *  g(x) (chain rule)
g(x) (chain rule)
 f(x)g(x) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g '(x) (product rule)
f(x)g(x) = f'(x)g(x) + f(x)g '(x) (product rule)
