Quote of the Day:
"The arithmetic of life does not always have a logical answer."
-- Inshirah Abdur-Rauf
Objectives:
The student will take derivatives of implicitly-defined functions.
The student will learn the definitions of orthogonal and normal
to a curve.
1. So far, the functions we have been working with have
been explicitly expressed in terms of one variable:
y = f(x) y = sin(x) y = 3x-5
We often see relations like these:
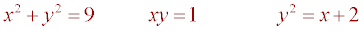 We can solve these for y in terms of x.
But there are some equations which we can not solve
for y:
We can solve these for y in terms of x.
But there are some equations which we can not solve
for y:
 These relations are said to be implicitly defined and we
can find their derivatives using implicit differentiation.
2. Examples:
These relations are said to be implicitly defined and we
can find their derivatives using implicit differentiation.
2. Examples:

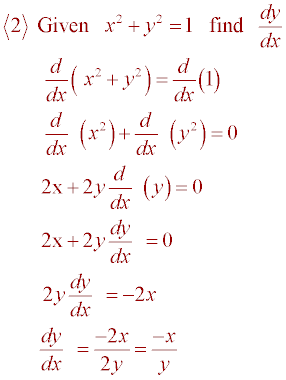 3. Define orthogonal curves:
Curves which are perpendicular to each other.
Define Normal to a curve
A normal to a curve is the line perpendicular to the
tangent line at that point.
Example:
3. Define orthogonal curves:
Curves which are perpendicular to each other.
Define Normal to a curve
A normal to a curve is the line perpendicular to the
tangent line at that point.
Example:
 4. Assignment:
p. 253 (1, 8, 12, 15, 17)
Worksheet on Implicit Differentiation
4. Assignment:
p. 253 (1, 8, 12, 15, 17)
Worksheet on Implicit Differentiation
Click here to go to the next page
We can solve these for y in terms of x. But there are some equations which we can not solve for y:
These relations are said to be implicitly defined and we can find their derivatives using implicit differentiation. 2. Examples:

3. Define orthogonal curves: Curves which are perpendicular to each other. Define Normal to a curve A normal to a curve is the line perpendicular to the tangent line at that point. Example:
4. Assignment: p. 253 (1, 8, 12, 15, 17) Worksheet on Implicit Differentiation